The PICASO project is developing an ICT platform to support coordination of care plans for people diagnosed
with co-occurring chronic diseases.
Better coordination of care plans between healthcare sectors is high on the European health agenda. So is
efficient management of the steadily rising number of patients with co-existing chronic conditions. The
PICASO project aims to develop information and communication technologies which meet these demands, by
supporting a continuum of care from hospitals and outpatient clinic to the home.
The PICASO platform will enable the sharing of a patient's complete care pathways with tools to establish
health status, predict risks and adjust care. Based on monitoring of different physiological parameters at
home, the patients can actively participate in their own care. The result is better management of co-existing
diseases and coordination of care plans for the benefit of patients and carers across organisations.
To demonstrate the platform and its wide applicability, the technologies will be trialled in two different national
settings with two different patient groups, involving 60 patients: in Italy, the University Hospital of Tor Vergata
in Rome will enrol patients with Parkinson's disease and in Germany, the University Hospital of Düsseldorf will
engage patients diagnosed with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Both patient groups have Cardiovascular Diseases as
co-morbidities and both settings share the complexity of treating co-occurring diseases, also known as
multimorbidities.
The trials will establish how PICASO can improve the exchange of data between stakeholders in the workflow
and validate the effect of PICASO on the care systems as well as the acceptance of the system by the wider
group of stakeholders such as patients, relatives and the society at large.
The technology

The PICASO platform is a service oriented, ICT-based integration platform based on an orchestration of care
services which is dynamic and personalised. The method for sharing patient information between all relevant
formal and informal care providers is by using a unique, trust-federated solution which overcomes the problem
of data privacy in cloud based health systems.
The platform consists of an Integrated Care Platform, a Data Management Platform and a Multi-Morbidity
Decision Tool:
The PICASO Integrated Care Platform;
- is an integration platform for sharing a patient’s complete care pathways across multi-actor care spaces with appropriate tools such as risk prediction models for the interpretation of patients’ immediate and future
health status, and the ability to dynamically adjust the content and management of the delivered care
services so they are always adapted to the patient’s personal health status and ability. - contains a robust, privacy compliant, cloud-based Resource Management system that can perform
acquisition of physiological and behavioural data in non-clinically controlled care spaces. - creates a new approach to integrated care, based on the concept of dynamic service narratives that define
the workflow (content and management of care services) to be launched and orchestrated across the
relevant care spaces. - provides decision support for multi-actor interaction, and enables patients and relatives to become active
participants.
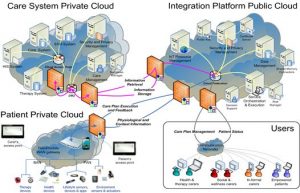
The PICASO Data Management Platform
- provides role-based access for carers to distribute shared data and exchange of knowledge about the
patient’s status in an intuitive collaborative platform. - provides a framework for secure, privacy-compliant, and role-based information sharing through a common
view of data, allowing carers to control and share patient information and exchange knowledge across care
networks, using intuitive, interactive ad-hoc information search.
The PICASO Multi-Morbidity Decision Support Tool;
- contains a decision support methodology for analysing conflicts, constraints and limitations from single-
morbidity care plans and patient/physician/therapist preferences applied to patients with comorbidities
and multimorbidity conditions. By using the concept of 'constraint satisfaction problem' whereby a number
of constraints or limitations are considered, the cares can define new care programmes for the management
of comorbidities in community and home care settings. - forms the basis for new training programmes for the care workforce, new organisational models and new
ways of exchanging medical information to improve the coordination of multimorbidity care management
across silos.